Mature Microservice Client Using J-Framework
This example demonstrates the usage of the j-framework in creating a mature microservice client.
Prerequisites:
-
You should have JDK 17+ Installed. (Click Here).
-
You should have a mature microservice running. (Click Here)
-
You should create a Maven Project.
-
You should enable snapshot versions. (Click Here).
Project Content:
This section contains what you should add to your code structure for this example.
-
Maven Project with pom.xml that has the following contents:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.jalalkiswani</groupId>
<artifactId>j-app-webstack</artifactId>
<version>7.0.2</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>j-framework-microservice-mature-client-example</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
</project>-
Java Model class is located at
src/main/java/com/app/person/Model.javathat has the following content:
package com.app.person;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Model implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String nationalId;
private String name;
private String email;
private String address;
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setNationalId(String nationalId) {
this.nationalId = nationalId;
}
public String getNationalId() {
return this.nationalId;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getEmail() {
return this.email;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getAddress() {
return this.address;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
return this.getId().equals(((Model) obj).getId());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (this.id == null) {
return toString().hashCode();
}
return this.id.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
buf.append(this.id).append(",");
buf.append(this.nationalId).append(",");
buf.append(this.name).append(",");
buf.append(this.email).append(",");
buf.append(this.address).append(",");
return buf.toString();
}
}-
Server URL Configuration file located at
src/main/resources/config.propertieswhich contains the following:
app.services.persons.url=http://localhost:8080/app/persons-
Main java class located at
src/main/java/com/app/App.javawhich contains the following:
package com.app;
import java.util.List;
import com.app.person.ExampleServiceClient;
import com.app.person.Model;
import com.jk.core.util.JK;
public class App {
private static Model createdAccount;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExampleServiceClient client = new ExampleServiceClient();
addRecord(client);
updateRecord(client);
printAll(client);
find(client);
delete(client);
// find(client); this will throw an exception with 404 page not found
}
private static void updateRecord(ExampleServiceClient client) {
createdAccount.setName("Updated - Jalal");
client.update(createdAccount);
}
private static void delete(ExampleServiceClient client) {
client.delete(createdAccount.getId());
}
private static void find(ExampleServiceClient client) {
// Retrieve single account
Model account = client.find("/" + createdAccount.getId());
JK.printBlock(account);
}
private static void addRecord(ExampleServiceClient client) {
Model account = new Model();
account.setNationalId("123456789");
account.setName("Jalal Kiswani");
account.setEmail("[email protected]");
account.setAddress("Reno, NV");
createdAccount= client.insert(account);
}
private static void printAll(ExampleServiceClient client) {
// Retrieve all account
List<Model> list = client.getAll();
for (Model record : list) {
JK.print(record);
}
}
}|
Alternatively, you can clone or download the tutorial repository then import the project into your IDE. |
How to run Project:
-
Set up the project with the content shown above.
-
Inside your IDE, go to the
src/main/java/com/app/App.javaclass.

-
Next, run it as a Java Application.

-
Your program will start running and show you the result of the run in the console.
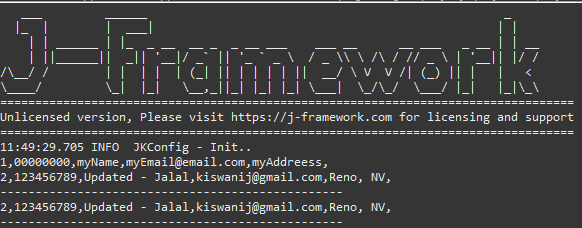
Example Explanation
-
The first two output lines are printing all the records inside the microservice, notice how the second record which got updated is changed.
-
The following line shows the record that got deleted.
-
Check the main method to see how the client and server communicated to produce this output.